Difference between revisions of "CLARIN/Security for web services"
(add shibboleth image) |
(add requirements distinction) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | == General requirements == | |
| − | + | The general delegation issue as [http://agenda.nikhef.nl/conferenceDisplay.py?confId=993 discussed before] has the following requirements. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| | {| | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| Line 30: | Line 28: | ||
(*) ''"Workshop security for web services - discussion minutes"'', W. van Engen, 2010 | (*) ''"Workshop security for web services - discussion minutes"'', W. van Engen, 2010 | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Specific requirements for this use-case == | ||
| + | The practical use-case that is being looked at is a lot simpler. Here a user logged into the [http://www.clarin.eu/cmdi CMDI] portal needs to be able to access private information in the [http://www.isocat.org/ ISOcat] registry. This means that logging into the CMDI portal should give access to the ISOcat registry as well. How exactly, that is the topic of this discussion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The requirements for this specific use-case are equal to the general case though a little simpler: | ||
| + | # Only one level of delegation is required: a single service should be accessed from the portal | ||
| + | # All user interaction is in the web-browser | ||
| + | # Delegation needs to happen only when the user is active in the portal (not offline) | ||
| + | |||
== Options == | == Options == | ||
Revision as of 12:29, 31 March 2011
General requirements
The general delegation issue as discussed before has the following requirements.
|
for the User
|
for Services
|
for the System as a whole |
Optional or variable criteria:
- Restrictions on delegation
- Performance / overhead
(*) "Workshop security for web services - discussion minutes", W. van Engen, 2010
Specific requirements for this use-case
The practical use-case that is being looked at is a lot simpler. Here a user logged into the CMDI portal needs to be able to access private information in the ISOcat registry. This means that logging into the CMDI portal should give access to the ISOcat registry as well. How exactly, that is the topic of this discussion.
The requirements for this specific use-case are equal to the general case though a little simpler:
- Only one level of delegation is required: a single service should be accessed from the portal
- All user interaction is in the web-browser
- Delegation needs to happen only when the user is active in the portal (not offline)
Options
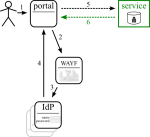
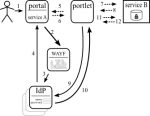
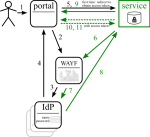
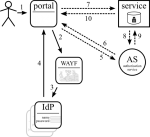
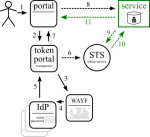
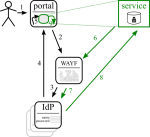
There are different ways of tackling the issue, but only some can survive. (In the diagrams solid lines are browser redirects, dashed lines are communication outside of the browser.)
Open
All services trust each other. No technical security measures (other than, possibly, blocking complete strangers); managable upto ~15 services [TODO ref needed]
Shibboleth + delegation
Shibboleth is already used for federated authentication. It has ECP support with delegation, though only through a plugin. The next major IdP release may include it though.
One cannot expect each IdP to install this plugin, or to have the latest version installed [TODO check if this is the case with Shibboleth version policies]. Therefore this option is not viable.
SAML ECP
(see Shibboleth) [TODO would there be other SAML ECP options than Shibboleth?]
OAuth 1.0
OAuth 1 is used on the world wide web as a method to access server resources on behalf of a resource owner. It is used by quite a number of big websites like Google, Twitter.
OAuth 1.0 requires browser redirection and confirmation [TODO check if confirmation is optional]. This might be acceptable for the portal scenario, but not for nested service invocations (real delegation).
OAuth 2.0
OAuth 2 is the next evolution of OAuth (still in draft), which supports many more scenario's. This is being adopted (Facebook is on the wagon already). RedIRIS has already made this work with Shibboleth in OAuth2lib. Here the AS is a token service that is populated by the portal.
Intermediate Token Portal
Expading on the OAuth 2.0 approach, one could decouple feeding the token service (STS, or AS in previous diagram) from the user portal: a dedicated portal (that is invisible to the user by redirects) could do this instead. This could improve security and make building portals easier.
Browser mashup
It may also be possible to keep the portal and service completely separated and combine them in the browser (the web mashup approach). As the service is in this case no more than a pick-list, it could be put in an iframe, which could somehow return a value to the parent document (some tricks required, but it may be possible). Authentication of the portal and the service is then completely unrelated, but single sign-on can make this a smooth experience.
This is not a general solution, but may be a simple solution for this specific case.
Links
Standards
- User Managed Access (UMA) has some overlap with this work
- OASIS Web Services Security: WS-Security, username, X.509, SAML
- A SASL and GSS-API Mechanism for SAML, uses base64 encoded SAML request in URL
- OAuth 2.0, and with SAML assertions
Libraries
- OAuth 2 assertion profile library
- Shibboleth ECP delegation, web-service client, and configuring it.