Difference between revisions of "Testbed Update Plan"
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
| If bleek is destined to be home directory server, VMWare should be put on other hardware. | | If bleek is destined to be home directory server, VMWare should be put on other hardware. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Data plan for precious data === | === Data plan for precious data === | ||
Revision as of 21:41, 20 February 2013
Planning the update of the middleware/development test bed
There is a number of tasks involved in bringing the testbed to where we like to be. We also need to agree on a timeframe in which we like to see these things accomplished.
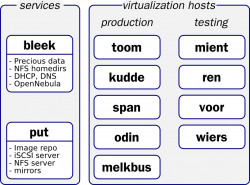
inventory of current services
This section should list the current services we run and use on the testbeds. For each service, we should explain what we should like to do with it (keep, drop, change?).
| Service | System | keep/move/lose | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDAP | span | lose | to be discontinued after migration to central LDAP |
| DHCP | span | move | by dnsmasq, /etc/hosts and /etc/ethers. Should migrate elsewhere |
| DHCP | bleek | keep | bleek is going to be the main home directory and DHCP server, after it's been upgraded. |
| Cruisecontrol | bleek | move | build system for VL-e and BiG Grid; may move to Hudson. Currently transferred to cruisecontrol.testbed |
| Hudson | kudde | move | continuous integration, currently for jGridstart but could serve others |
| Home directories | everywhere | move | should be merged onto single NFS server |
| X509 host keys and pre-generated SSH keys | span | move | all in /var/local/hostkeys |
| Robot certificate (etoken) | kudde | keep/move | hardware token is plugged into kudde to generate vlemed robot certificates using cronjob + software in /root/etoken. Token can be moved to another machine but it should remain within the P4CTB |
| VMWare Server 1.0 | bleek | move | If bleek is destined to be home directory server, VMWare should be put on other hardware. |
Data plan for precious data
Precious means anything that took effort to put together, but nothing that lives in version control elsewhere. Think home directories, system configurations, pre-generated ssh host keys, X509 host certs, etc.
One idea is to put all of this on a box that is not involved in regular experimentation and messing about, and have backup arranged from this box to Sara with ADSM (which is the current service running on bleek). After this is arranged we begin to migrate precious data from all the other machines here, leaving the boxen in a state that we don't get sweaty palms over scratching and reinstalling them.
Hardware inventory
Perhaps this should be done first. Knowing what hardware we have is prerequisite to making sensible choices about what we try to run where.
Changes here should probably also go to NDPF System Functions.
| name | ipmi name* | type | chipset | #cores | mem | OS | disk | service tag | remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bleek | bleek | PE1950 | Intel 5150 @2.66GHz | 4 | 8GB | CentOS4-64 | software raid1 2×500GB disks | CQ9NK2J | High Availability, dual power supply; precious data; backed up |
| toom.testbed | toom | PE1950 | Intel E5440 @2.83GHz | 8 | 16GB | CentOS5-64 | Hardware raid1 2×715GB disks | DC8QG3J | current Xen 3 hypervisor with mktestbed scripts |
| kudde | kudde | PE1950 | Intel E5440 @2.83GHz | 8 | 16GB | CentOS5-64 | Hardware raid1 2×715GB disks | CC8QG3J | Contains hardware token/robot proxy for vlemed; current Xen 3 hypervisor with mktestbed scripts |
| span | span | PE2950 | Intel E5440 @2.83GHz | 8 | 24GB | CentOS5-64 | Hardware raid10 on 4×470GB disks (950GB net) | FP1BL3J | DHCP,DNS,NFS,LDAP; home dirs must be moved to bleek; current Xen 3 hypervisor with mktestbed scripts |
| melkbus | hals | PEM600 | Intel E5450 @3.00GHz | 8 | 32GB | CentOS5-64 | 2x 320GB SAS disks | 76T974J | to be renamed to hals; Oscar's private machine? |
| put.testbed | put | PE2950 | HMXP93J | former garitxako;FreeNAS | |||||
| blade14.testbed | bl0-14 | PEM610 | Intel E5504 @2.00GHz | 2x4 | 16GB | OVMS 3.0.3 | 4NZWF4J | former autana | |
| blade13.testbed | bl0-13 | PEM610 | 5NZWF4J | former arauca; OVM 3.0.3 | |||||
| voor | arrone | PE1950 | 982MY2J | former arrone; status unclear; Jan Just? | |||||
| wiers | aulnes | PE1950 | B82MY2J | former aulnes; status unknown | |||||
| ent | (no ipmi) | Mac Mini | Intel Core Duo @1.66GHz | 2 | 2GB | OS X 10.6 | SATA 80GB | OS X box (no virtualisation) |
- *ipmi name is used for IPMI access; use
<name>.ipmi.nikhef.nl. - System details such as serial numbers can be retrieved from the command line with
dmidecode -t 1. - The service-tags can be retrieved through IPMI, but unless you want to send raw commands with ipmitool first you need freeipmi-tools. This contains ipmi-oem that can be called thus:
ipmi-oem -h host.ipmi.nikhef.nl -u username -p password dell get-system-info service-tag
IPMI serial-over-LAN
- For details, see Serial Consoles. The setup for Debian squeeze is slightly different.
- can be done by
ipmitool -I lanplus -H name.ipmi.nikhef.nl -U user sol activate. - SOL access needs to be activated in the BIOS once, by setting console redirection through COM2.
For older systems that do not have a web interface for IPMI, the command-line version can be used. Install the OpenIPMI service so root can use ipmitool. Here is a sample of commands to add a user and give SOL access.
ipmitool user enable 5 ipmitool user set name 5 ctb ipmitool user set password 5 '<blah>' ipmitool channel setaccess 1 5 ipmi=on # make the user administrator (4) on channel 1. ipmitool user priv 5 4 1 ipmitool channel setaccess 1 5 callin=on ipmi=on link=on ipmitool sol payload enable 1 5
Serial over LAN for hardware running Debian squeeze
On Debian squeeze you need to tell grub2 what to do with the kernel command line in the file /etc/default/grub. Add or uncomment the following settings:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="" GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="console=tty0 console=ttyS1,115200n8" GRUB_TERMINAL=console GRUB_SERIAL_COMMAND="serial --speed=115200 --unit=1 --word=8 --parity=no --stop=1"
Then run update-grub.
Data Migration
Bleek.nikhef.nl is designated to become the home directory server, DHCP server and OpenNebula server. It will be the only persistent machine in the entire testbed, the rest should be considered volatile. It will be the only machine where backups are done. But before all this can be arranged, it needs to be reinstalled with CentOS 5 (currently CentOS 4). All important data and configurations are going to be migrated to span.nikhef.nl as an intermediate step, and after the upgrade this will be moved back and merged on bleek.
Disk space usage on bleek (in kB):
50760 etc 317336 lib 432640 opt 877020 export 1035964 root 2353720 var 3258076 usr 357844380 srv
There is a script in place on span.nikhef.nl to do the backup from bleek, where /etc/rsyncd.conf is already set up.
rsync -a --password-file /etc/rsync-bleek-password --exclude /sys** --exclude /proc** --delete --delete-excluded bleek::export-perm /srv/backup/bleek/
It's not run automatically, so it should be run manually at the very latest right before reinstalling bleek.
Cruisecontrol migration
The former cruisecontrol instance on bleek has been stopped. The service has ben transferred to cruisecontrol.testbed(toom.nikhef.nl), while the data in /srv/project/rpmbuild has been transferred to span.nikhef.nl and is exported from there with NFS.
Network plan
There are three VLANs in use. All the physical machines (i.e. the hypervisors, Dom0 in Xen terminology) should configure bridges for all three; virtual machines then get interfaces for any combination depending on their role.
| vlan | description | network | gateway | ACL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | P4CTB | 194.171.96.16/28 | 194.171.96.30 | No inbound traffic on privileged ports |
| 8 | Open/Experimental | 194.171.96.32/27 | 194.171.96.62 | Open |
| untagged | local | 10.198.0.0/16 | testbed only |
Since there is limited public IP available, we should put machines in the local network as much as possible. For outbound connectivity NATting is arranged via their Dom0.
The machines that run Xen 3.0 on CentOS 5 use the following configuration for networking:
/etc/sysconfig/network:
NETWORKING=yes NETWORKING_IPV6=yes HOSTNAME=span FORWARD_IPV4=yes NOZEROCONF=true GATEWAY=194.171.96.30 GATEWAYDEV=eth0.2
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0:
TYPE=Ethernet DEVICE=eth0 HWADDR=00:1e:4f:xx:xx:xx BOOTPROTO=none ONBOOT=yes USERCTL=no IPV6INIT=no IPV4INIT=yes NETMASK=255.255.0.0 IPADDR=10.198.x.y
(Fill in the mac address of the actual hardware, and the 10.198.0.0 network config for the machine.)
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0.2:
VLAN=yes DEVICE=eth0.2 BOOTPROTO=static ONBOOT=yes TYPE=Ethernet NETMASK=255.255.255.240 IPADDR=194.171.96.x USERCTL=no IPV6INIT=no IPV4INIT=yes
This should result in a working network configuration before the start of the Xen daemon.
The Xen network scripts to use require an additional script to configure a VLAN bridge without any virtual network devices on it. The file /etc/xen/xend-config.sxp should have:
(network-script 'network-multi-vlan') (vif-script vif-bridge bridge=xenbr2)
And the script /etc/xen/scripts/network-multi-vlan contains: dir=$(dirname "$0")
"$dir/network-bridge" "$@" vifnum=0 "$dir/network-bridge" "$@" vifnum=2 netdev=eth0.2 "$dir/network-bridge-vlan" "$@" vlan=8 netdev=peth0
The network-bridge-vlan is non-standard; it creates a vlan interface, binds it to a bridge but leaves it unconfigured otherwise. This way the Dom0 doesn't have a Open/Experimental interface itself, but DomUs can connect their vifs to the bridge. The xen scripts are fairly complicated in the way they rename interfaces and transfer addresses and routes to the virtual counterparts; in case things go wrong, diagnostic information may be obtained from:
brctl show cat /proc/net/vlan/* ip link show netstat -rn
but be awary that the Xen scripts actually rename interfaces to make them look like normal ones.
All systems have at least 1GB interface, but put has two which may be trunked. This could be useful for serving machine images. The blade systems have extra interfaces and may be capable of doing iSCSI offloading to the NIC.
TODO: draw a network lay-out.
LDAP migration
We're going to ditch our own directory service (it served us well, may it rest in peace) in favour of the central Nikhef service. This means changing user ids in some (all?) cases which should be done preferable in a single swell foop.
We should request to add a testbed 'service' to LDAP with ourselves as managers, so we can automatically populate /root/.ssh/authorized_keys.
Here's a simple example of an ldapsearch call to find a certain user.
ldapsearch -x -H ldaps://hooimijt.nikhef.nl/ -b dc=farmnet,dc=nikhef,dc=nl uid=dennisvd
And here is the ldap.conf file to use for ldap authentication.
base dc=farmnet,dc=nikhef,dc=nl timelimit 120 bind_timelimit 120 idle_timelimit 3600 nss_initgroups_ignoreusers root,ldap,named,avahi,haldaemon,dbus,radvd,tomcat,radiusd,news,mailman uri ldaps://gierput.nikhef.nl/ ldaps://hooimijt.nikhef.nl/ ldaps://stalkaars-01.farm.nikhef.nl/ ldaps://stalkaars-03.farm.nikhef.nl/ ldaps://vlaai.nikhef.nl/ ssl on tls_cacertdir /etc/openldap/cacerts
Migration to a cloud infrastructure
Previous testbed cloud experiences are reported here.
Currently, using plain libvirt seems to fit most of our needs.
The machines blade13 and blade14 are setup with Debian squeeze, libvirt and KVM with a Fiber Channel link to the compellent storage over which clustered LVM is defined to share access to the pool.
The machines arrone and aulnes are setup with Debian squeeze, libvirt and KVM with an NFS storage backend on put.testbed (storage.testbed) over which clustered LVM is defined to share access.
It happens that on reboot of a machine you need to manually start the pool and/or run vgscan. It is unclear at this moment why this would happen.
virsh pool-start vmachines
error: Failed to start pool vmachines error: internal error '/sbin/vgchange -ay vmachines' exited with non-zero status 5 and signal 0: Error locking on node arrone.testbed: Volume group for uuid not found: hI7udF9MvGpKkvkympcNG42glpwtwDeqhv7xV9wKHHdv9tDxQ9j8Lhgqem1esMcA
The following sequence of commands can be useful:
vgscan
Reading all physical volumes. This may take a while... Found volume group "vmachines" using metadata type lvm2
virsh pool-start vmachines
Pool vmachines started
virsh pool-list --all
Name State Autostart ----------------------------------------- default active yes put.testbed active yes vmachines active yes
Also check the state of the LVM cluster, logs are in /var/log/cluster/. In the (rare) case the fence daemon has blocked the use of the cluster, the other machine in the cluster must be told it is ok to release the block. What the other machine is can be found in /etc/cluster/cluster.conf.
fence_ack_manual other-machine
Installing clustered lvm for live migration
The machines arrone.testbed and aulnes.testbed, running Debian stable, are now equipped with a clustered LVM setup with an iSCSI device as the backend storage. The iSCSI device is served by put.testbed running FreeNAS.
Documentation to set up CLVM is available for Red Hat and Debian, both should be comparable.
First, a cluster needs to be defined and all systems in the cluster need to use the same definition. Put the file in /etc/cluster/cluster.conf:
<cluster name="vmachines" config_version="1">
<cman expected_votes="1" two_node="1">
</cman>
<clusternodes>
<clusternode name="arrone.testbed" votes="1" nodeid="1">
<fence>
</fence>
</clusternode>
<clusternode name="aulnes.testbed" votes="1" nodeid="2">
<fence>
</fence>
</clusternode>
</clusternodes>
<logging to_syslog="yes" to_logfile="yes" syslog_facility="daemon" syslog_priority="info">
</logging>
<fence_daemon post_join_delay="30" />
<totem rrp_mode="none" secauth="off"/>
</cluster>
The setting 'two_node' is a special case for two node clusters, because there is no sensible way to do majority voting. In case one of the machines fails, the other will block to fence the first machine (which is a manual operation in our case) but the cluster can carry on with just one machine if needs be.
The machines keep an eye on one another through multicast, and therefore it is important to remove the following line from /etc/hosts:
127.0.1.1 arrone.testbed
which the Debian installation inserted. This makes the cluster manager daemon bind the wrong device for multicasts (the loopback device).
Another snag found on installation is the missing directory /var/run/lvm, which causes the startup script of clvm to fail. Once this is fixed, run
/etc/init.d/cman start /etc/init.d/clvm start
Finally, the file
/etc/lvm/lvm.conf
needs to be edited to set
locking_type = 3
in order to use clustered locking.
Through this shared storage it is possible to do live migration of virtual machines between arrone and aulnes.
Installing Debian on blade 13 and 14 with Fiber Channel
This is a quick note to record a recent quirk. Although FC support on Debian works fine, using the multipath-tools-boot package is a bit tricky. It will update the initrd to include the multipath libraries and tools, to make it available at boot time.
This happened on blade-13; on reboot it was unable to mount the root partition (The message was 'device or resource busy') because the device mapper had somehow taken hold of the SCSI disk. By changing the root=UUID=xxxx stanza in the GRUB menu to root=/dev/dm-2 (this was guess-work) I managed to boot the system. There were probably several remedies to resolve the issue:
- rerun update-grub. This should replace the UUID= with a link to /dev/mapper/xxxx-part1
- blacklist the disk in the device mapper (and running mkinitramfs)
- remove the multipath-tools-boot package altogether.
I opted for blacklisting; this is what's in /etc/multipath.conf:
blacklist {
wwid 3600508e000000000d6c6de44c0416105
}
A bonnie test of a VM with disk on local disk vs. a VM with disk on FC:
- lofarwn.testbed had its disk locally
Version 1.03e ------Sequential Output------ --Sequential Input- --Random-
-Per Chr- --Block-- -Rewrite- -Per Chr- --Block-- --Seeks--
Machine Size K/sec %CP K/sec %CP K/sec %CP K/sec %CP K/sec %CP /sec %CP
lofarwn 4G 20869 35 30172 5 23198 6 45957 85 510971 84 +++++ +++
------Sequential Create------ --------Random Create--------
-Create-- --Read--- -Delete-- -Create-- --Read--- -Delete--
files /sec %CP /sec %CP /sec %CP /sec %CP /sec %CP /sec %CP
16 16759 99 +++++ +++ +++++ +++ 16810 100 +++++ +++ +++++ +++
lofarwn,4G,20869,35,30172,5,23198,6,45957,85,510971,84,+++++,+++,16,16759,99,+++++,+++,+++++,+++,16810,100,+++++,+++,+++++,+++
- ige-cert.testbed has disk on LVM via FC.
Version 1.03e ------Sequential Output------ --Sequential Input- --Random-
-Per Chr- --Block-- -Rewrite- -Per Chr- --Block-- --Seeks--
Machine Size K/sec %CP K/sec %CP K/sec %CP K/sec %CP K/sec %CP /sec %CP
ige-cert 4G 53384 96 216611 37 102283 24 51060 95 689474 79 +++++ +++
------Sequential Create------ --------Random Create--------
-Create-- --Read--- -Delete-- -Create-- --Read--- -Delete--
files /sec %CP /sec %CP /sec %CP /sec %CP /sec %CP /sec %CP
16 12676 100 +++++ +++ +++++ +++ 12761 99 +++++ +++ +++++ +++
ige-cert,4G,53384,96,216611,37,102283,24,51060,95,689474,79,+++++,+++,16,12676,100,+++++,+++,+++++,+++,12761,99,+++++,+++,+++++,+++