Difference between revisions of "DAQ systems: Genesys"
(arrange the pictures and links) |
m (rearrange infos) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Author: Andrea García Alonso aalonso@nikhef.nl | |
| − | + | <math>\blacktriangleleft</math> [[ITk Endcap Homepage|''<big>Back to ITk End-cap Homepage</big>'']] | |
| + | ---- | ||
| − | + | For petal reception, two setups are required: FELIX (the one ATLAS will use) and Genesys (the one used by the petal production sites before shipment to Nikhef). Genesys doesn't require servers and it's more simple than FELIX. | |
| − | + | '''Useful links:''' | |
| − | + | - About the Genesys2 card: https://twiki.cern.ch/twiki/bin/view/Atlas/Genesys2ITSDAQ | |
| − | + | - ITSDAQ firmware: https://www.hep.ucl.ac.uk/~warren/upgrade/firmware/?C=M;O=D | |
| − | + | - Firmware: https://www.hep.ucl.ac.uk/~warren/upgrade/firmware/genesys2_itsdaq_vc5f0_FDP_STAR.bit | |
| − | |||
| + | - ITSDAQ software: https://gitlab.cern.ch/atlas-itk-strips-daq/itsdaq-sw | ||
| − | + | - Documentation of the ITSDAQ software: https://atlas-strips-itsdaq.web.cern.ch (previous tracker documentation was called SCTDAQ and sometimes names may be mixed along the documentation). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | [[File:Punit 20221013 131437.jpg|none|thumb|402x402px|Genesys setup at SR1. Picture by Punit Sharma ([[Mailto:punit.sharma@cern.ch|punit.sharma@cern.ch]]) 14/10/2022]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Setups at Nikhef and how to configure the Genesys setup = | ||
| + | |||
| + | === R5 PPB Petal setup === | ||
| + | If you have a fully loaded petal, follow these instructions: [[ITSDAQ for full petals]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Single module setup (first and oldest setup) === | ||
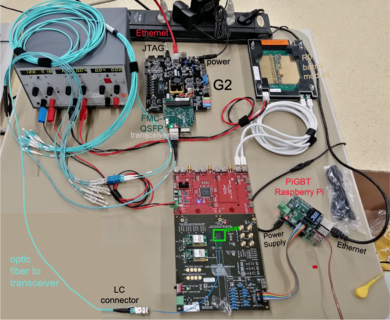
| + | Working chain with VLDB+ and Nikhef adapter board: G2 --> FMC-QSFP --> VLDB+ --> Adapter Board --> Module.Genesys setup at lab N221 at Nikhef, mounted on 31st October 2022, consisting of a Genesys2 with FMC-QSFP and transceiver connected to the module through the VLDB+ and the adapter board which have the role of an EoS card: | ||
| + | [[File:ITk-server labN221 20221207 1132-2.jpg|thumb|380x380px|ITk-server in Nikhef lab N221. It will be moved to the cleanroom when petals arrive to Amsterdam. In this picture, both FELIX (through blue fibers) and Genesys (through red ethernet cable) are connected to this server|alt=|left]] | ||
| + | [[File:Genesys setup NIkhef 31-10-22.png|thumb|390x390px|Genesys setup mounted on 31/10/2022 in lab N221 at Nikhef. The whole setup is shown in the picture (no servers involved as in the case of FELIX)|alt=|center]] | ||
| − | |||
After installing the firmware and software, the server and Genesys must be able to communicate if the IP addresses are set correctly. You can check this with: | After installing the firmware and software, the server and Genesys must be able to communicate if the IP addresses are set correctly. You can check this with: | ||
| Line 26: | Line 35: | ||
<code>ifconfig</code> | <code>ifconfig</code> | ||
| − | + | The Genesys is connected to the second ethernet interface eno2 of the ITk server (see the red ethernet cable going to the ITk server in the picture, which after September 2024 is not red anymore, but same stuff). | |
| + | |||
| + | The IP on eno2 has to be the same as the one shown on the display of the Genesys (192.168.222.16 for my Genesys), but changing the last digits, for example: 192.168.222.10. You can modify this in: | ||
| + | |||
| + | - In CentOS 7 (old): <code>vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eno2</code> | ||
| − | <code> | + | - In Alma Linux 9: <code>sudo nmcli connection modify eno2 ipv4.addresses 192.168.222.16</code> |
For the changes to take effect, you have to restart the network with the command: | For the changes to take effect, you have to restart the network with the command: | ||
| − | <code>sudo /etc/init.d/network restart</code> | + | - In CentOS 7 (old): <code>sudo /etc/init.d/network restart</code> |
| + | |||
| + | - In Alma Linux 9: <code>sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Create the directory: sctdaq/sctvar/config/ and inside of it, create these folders: <code>config/</code> <code>data/</code> <code>etc/</code> <code>ps/</code> <code>results/</code>. | ||
| − | + | Copy all the configuration files from <code>itsdaq-sw/config</code> to <code>/sctdaq/sctvar/config/</code> and execute the following commands: | |
cd itsdaq-sw | cd itsdaq-sw | ||
| − | (cd /cvmfs/sft.cern.ch/lcg/ | + | (cd /cvmfs/sft.cern.ch/lcg/releasess; lcgenv/latest/lcgenv -p LCG_96python3 x86_64-centos7-gcc8-opt ROOT) > env_file |
source ./env_file | source ./env_file | ||
export BOOSTDIR=$BOOST__HOME/include | export BOOSTDIR=$BOOST__HOME/include | ||
| + | For CentOS 7 (old) we used this setup.sh: | ||
source /cvmfs/sft.cern.ch/lcg/views/LCG_100/x86_64-centos7-gcc8-opt/setup.sh | source /cvmfs/sft.cern.ch/lcg/views/LCG_100/x86_64-centos7-gcc8-opt/setup.sh | ||
| + | But for Alma Linux 9, ROOT versions compatible with alma 9 are somewhat weird in the the sense that the interactive part does not work. However, use the following one (provided by Peter Philips), which is a patched version of root 6.26 that gives the complete functionality.: | ||
| + | source /cvmfs/sft.cern.ch/lcg/views/LCG_102b_ATLAS_11a/x86_64-centos9-gcc11-opt/setup.sh | ||
| + | |||
python waf configure | python waf configure | ||
python waf build | python waf build | ||
| Line 50: | Line 71: | ||
The following GUI will be opened: | The following GUI will be opened: | ||
[[File:GUI.png|none|thumb|1277x1277px|GUI that opens after executing RUNITSDAQ]] | [[File:GUI.png|none|thumb|1277x1277px|GUI that opens after executing RUNITSDAQ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <code>lpGBTAutoSetup()</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>lpgbtAuto_setPolarityCheck(0)</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>lpgbtAuto_setPolarityCheck(1)</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>AMAC_DCDC(-1,1)</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Notes and troubleshooting == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Up-to-date version of itsdaq-sw''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check the last version of the repo in: https://gitlab.cern.ch/atlas-itk-strips-daq/itsdaq-sw/-/tree/master?ref_type=heads | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Connectivity issues''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check the network configuration file: <code>sudo vim /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/eno2.nmconnection</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | And make sure that the eno2 address is different to the one of the G2 board. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, eno2 should have IP address <code>192.168.222.10</code> instead of <code>192.168.222.16</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the changes to take effect, it's necessary to restart the network: <code>sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''UDP socket creation failed because the address is already in use''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | First, identify which process is using the ports (in my case 60000 and 60001): | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo lsof -i :60000</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the process using these ports is not required, you can stop it. Note the PID (Process ID) from the previous command and kill the process: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>sudo kill -9 <PID></code> | ||
-- Main.AndreaGarciaAlonso - 2022-10-20 | -- Main.AndreaGarciaAlonso - 2022-10-20 | ||
Latest revision as of 12:04, 30 October 2024
Author: Andrea García Alonso aalonso@nikhef.nl
For petal reception, two setups are required: FELIX (the one ATLAS will use) and Genesys (the one used by the petal production sites before shipment to Nikhef). Genesys doesn't require servers and it's more simple than FELIX.
Useful links:
- About the Genesys2 card: https://twiki.cern.ch/twiki/bin/view/Atlas/Genesys2ITSDAQ
- ITSDAQ firmware: https://www.hep.ucl.ac.uk/~warren/upgrade/firmware/?C=M;O=D
- Firmware: https://www.hep.ucl.ac.uk/~warren/upgrade/firmware/genesys2_itsdaq_vc5f0_FDP_STAR.bit
- ITSDAQ software: https://gitlab.cern.ch/atlas-itk-strips-daq/itsdaq-sw
- Documentation of the ITSDAQ software: https://atlas-strips-itsdaq.web.cern.ch (previous tracker documentation was called SCTDAQ and sometimes names may be mixed along the documentation).

Setups at Nikhef and how to configure the Genesys setup
R5 PPB Petal setup
If you have a fully loaded petal, follow these instructions: ITSDAQ for full petals.
Single module setup (first and oldest setup)
Working chain with VLDB+ and Nikhef adapter board: G2 --> FMC-QSFP --> VLDB+ --> Adapter Board --> Module.Genesys setup at lab N221 at Nikhef, mounted on 31st October 2022, consisting of a Genesys2 with FMC-QSFP and transceiver connected to the module through the VLDB+ and the adapter board which have the role of an EoS card:
After installing the firmware and software, the server and Genesys must be able to communicate if the IP addresses are set correctly. You can check this with:
ifconfig
The Genesys is connected to the second ethernet interface eno2 of the ITk server (see the red ethernet cable going to the ITk server in the picture, which after September 2024 is not red anymore, but same stuff).
The IP on eno2 has to be the same as the one shown on the display of the Genesys (192.168.222.16 for my Genesys), but changing the last digits, for example: 192.168.222.10. You can modify this in:
- In CentOS 7 (old): vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eno2
- In Alma Linux 9: sudo nmcli connection modify eno2 ipv4.addresses 192.168.222.16
For the changes to take effect, you have to restart the network with the command:
- In CentOS 7 (old): sudo /etc/init.d/network restart
- In Alma Linux 9: sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager
Create the directory: sctdaq/sctvar/config/ and inside of it, create these folders: config/ data/ etc/ ps/ results/.
Copy all the configuration files from itsdaq-sw/config to /sctdaq/sctvar/config/ and execute the following commands:
cd itsdaq-sw (cd /cvmfs/sft.cern.ch/lcg/releasess; lcgenv/latest/lcgenv -p LCG_96python3 x86_64-centos7-gcc8-opt ROOT) > env_file source ./env_file export BOOSTDIR=$BOOST__HOME/include
For CentOS 7 (old) we used this setup.sh:
source /cvmfs/sft.cern.ch/lcg/views/LCG_100/x86_64-centos7-gcc8-opt/setup.sh
But for Alma Linux 9, ROOT versions compatible with alma 9 are somewhat weird in the the sense that the interactive part does not work. However, use the following one (provided by Peter Philips), which is a patched version of root 6.26 that gives the complete functionality.:
source /cvmfs/sft.cern.ch/lcg/views/LCG_102b_ATLAS_11a/x86_64-centos9-gcc11-opt/setup.sh
python waf configure python waf build python waf install export SCTDAQ_VAR=/home/aalonso/sctdaq/sctvar/config export SCTDB_USER=0001 ./RUNITSDAQ.sh
Once everything is set correctly, the commands configure, build and install no longer need to be executed.
The following GUI will be opened:
lpGBTAutoSetup()
lpgbtAuto_setPolarityCheck(0)
lpgbtAuto_setPolarityCheck(1)
AMAC_DCDC(-1,1)
Notes and troubleshooting
Up-to-date version of itsdaq-sw
Check the last version of the repo in: https://gitlab.cern.ch/atlas-itk-strips-daq/itsdaq-sw/-/tree/master?ref_type=heads
Connectivity issues
Check the network configuration file: sudo vim /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/eno2.nmconnection
And make sure that the eno2 address is different to the one of the G2 board.
For example, eno2 should have IP address 192.168.222.10 instead of 192.168.222.16
For the changes to take effect, it's necessary to restart the network: sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager
UDP socket creation failed because the address is already in use
First, identify which process is using the ports (in my case 60000 and 60001):
sudo lsof -i :60000
If the process using these ports is not required, you can stop it. Note the PID (Process ID) from the previous command and kill the process:
sudo kill -9 <PID>
-- Main.AndreaGarciaAlonso - 2022-10-20